What is time complexity ?
Ans: Time complexity not a run time of a code, its totally depends on system configuration, processor, server , input size will increase time complexity.
Time complexity ko likhne ke tarike jo hote hai use notation kehte hai.
Notation is basically symbol
NOTATION OF COMPLEXITY
Best Case: kam se kam time me chla gya code best case hota hai
Ω (Omega) Ω(1) se likhte hai
Average Case: Ek average time jisme code chle
Θ(n+1)/2
Worst Case: Worst case ka mtlb kuch bhi ho jaye is time ko ye exceed nhi kregea
O(n)
O(1) - Constant Time:
- Operations that take a constant amount of time, regardless of the size of the input data.
O(log n) - Logarithmic Time:
- Algorithms that have a logarithmic time complexity, often seen in binary search or certain tree-based algorithms. This is best time Complexity this is near from constant time
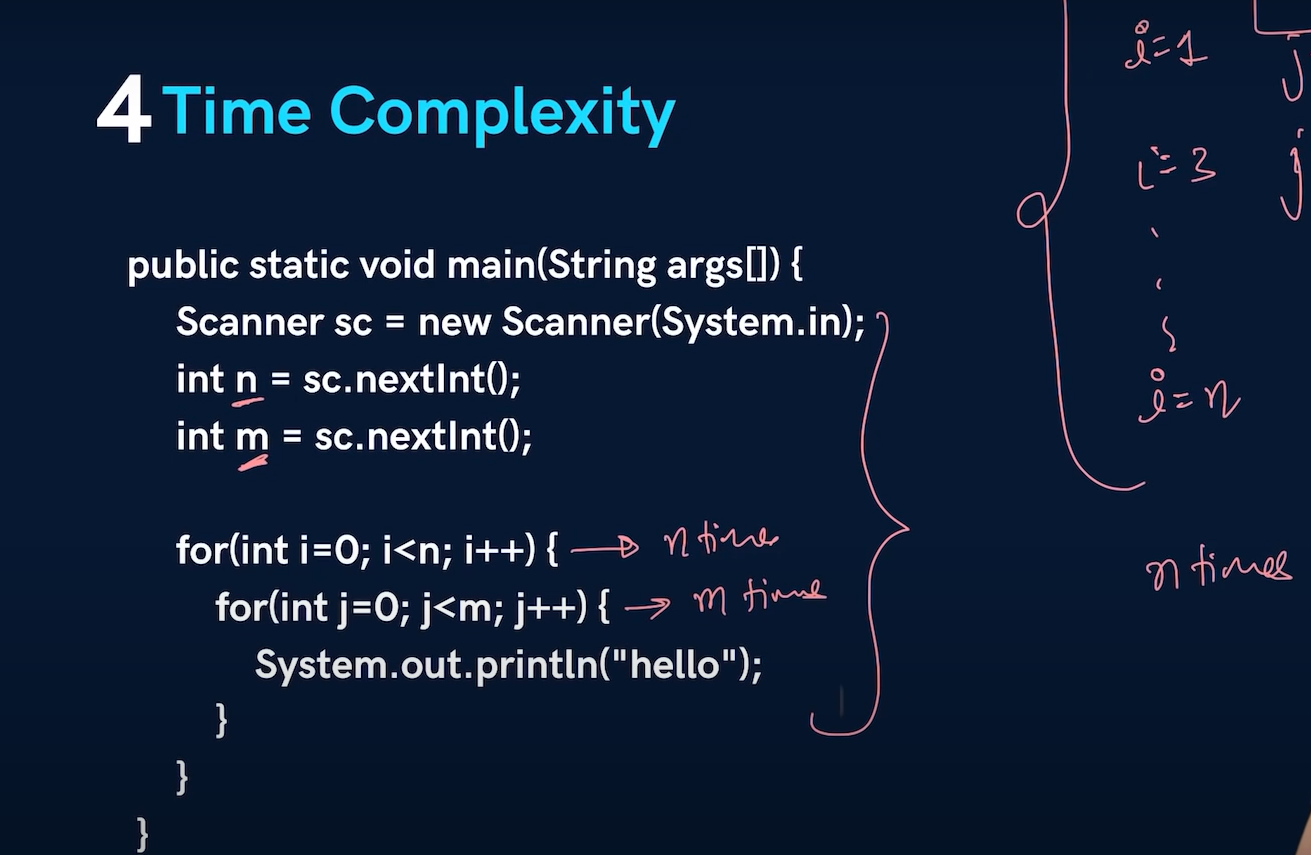
O(n) - Linear Time:
- The running time of the algorithm grows linearly with the size of the input.
O(n log n) - Linearithmic Time:
- Common in efficient sorting algorithms like mergesort and heapsort. or already inbuild sorting method like Array.sort
O(n^2) - Quadratic Time:
- Algorithms where the running time is proportional to the square of the size of the input.
O(2^n) - Exponential Time:
- Algorithms where the running time doubles with each additional element in the input. this is on recursion , This is generally brute force approach and this is bad time Complexity, to improve this will use dynammic programming technique
O(n!) - Factorial Time:
- Algorithms where the running time grows factorially with the size of the input. this is worst of all, ye sabse bura hota hai
Sabse least logn hota hai
>>> time complexity of all searching and sorting algorithm
1) Sabse chota hota hai logn
2) uske bad n logn
3) n
4) n2




Comments
Post a Comment