Question: What is Arraylists and why to use Arraylist ?
Ans: As you know, an array is one data structure we have been using till now. A major drawback of an array is that we have to specify its size. However, in scenarios where we need an array that can dynamically adjust or increase in size, we can use an ArrayList.
if u want to use Arraylist, we have to import arraylist package, just like scanner
import java.util.ArrayList; //this is arraylist
public class ArrayListDemo {
}
Array list just like a Generic class of oops, Java me Generic Class ek class hoti hai jise aap ek ya multiple data types ke saath use kar sakte hain. Generic classes allow you to create classes that can work with different types without sacrificing type safety. In other words, a generic class can be parameterized with different data types.
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String [] args){
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); //this is arraylist // this is object of an Arraylist
// ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<String>(); // this is String type ArrayList, Variable name is list2
list1.add(20);
System.out.println(list1);
}
}
This is object bcse we are using new keyword.
list1 is variable name and if we want to add add array on array list we need to use .add keyword and then in parentheses we can put value.
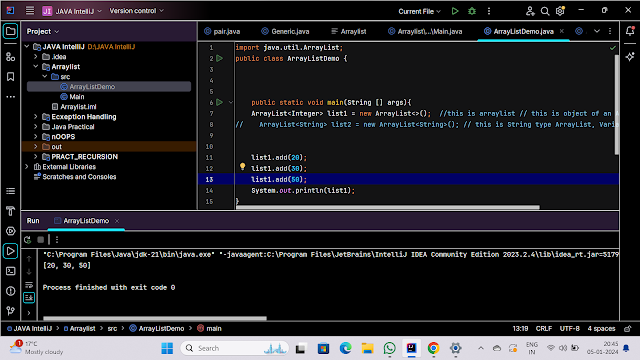
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String [] args){
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); //this is arraylist // this is object of an Arraylist
// ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<String>(); // this is String type ArrayList, Variable name is list2
list1.add(20);
list1.add(30);
list1.add(50);
System.out.println(list1);
System.out.println(list1.get(2)); // if u want to print any specific index element then use .get keyword
}
}
Note: if you want to print any specific index element in arrayLists then u can use this keyword list1.get(indexNumber));
Add element on Specific Index;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String [] args){
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); //this is arraylist // this is object of an Arraylist
// ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<String>(); // this is String type ArrayList, Variable name is list2
list1.add(20);
list1.add(30);
list1.add(50);
list1.add(2,99); //for add element in specific index where 2 is index and 99 is element
System.out.println(list1);
System.out.println(list1.get(2)); // if u want to print any specific index element then use .get keyword
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < list1.size();i++){
System.out.println(list1.get(i)); //this will print ith index element
}
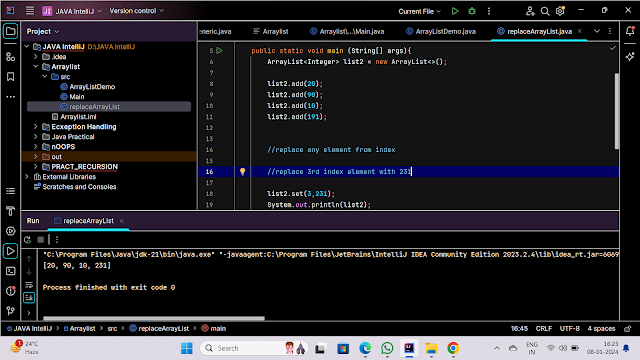
REPLACE AN INTEGER FROM ANY INDEX::
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class replaceArrayList {
public static void main (String[] args){
ArrayList<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.add(20);
list2.add(90);
list2.add(10);
list2.add(191);
//replace any element from index
//replace 3rd index element with 231
list2.set(3,231);
System.out.println(list2);
}
}

Comments
Post a Comment